1. Customer Concepts![]()
2. Why Bother
3. Sales and Marketing Overview
4. Marketing Basics
5. Sales Basics
6. Issues of Sales
7. Issues of your Role as a Salesman
8. Selling Situations
9. Pain Questions
10. You have to Get Paid
11. Rules
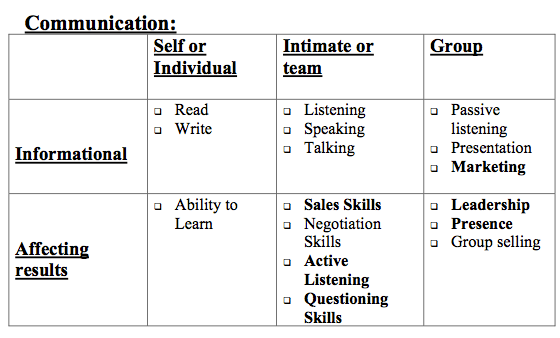
Having these communication skills in the core team is vital to a venture’s success.
1.Customer Concepts:
In most business interactions, there is a buyer and a seller. The buyer is called a “prospect” until he buys the first time. After this, he is your “customer”.
Who are your customers? Know them!
- Your immediate customer
- Your Boss’s customer
- Your department’s customer
- Your Company’s customer
• Your customer is the Person(s) who is the recipient of your product or service.
• You are probably a customer of other’s products and services.
• Be aware of what role you are playing in every interaction.
Customers are Not right or wrong, they are happy or unhappy!!
Unhappy Customers don’t pay
Unhappy customers don’t repeat
Get independent surveys of your customer’s happiness. Be sure to act on them.
For most of you, your customers are internal to the organization. Treat them the same as an external customer, and you win big.
2.Why Bother?
There are three types of communication in intimate (one-on-one or small group) interactions:
1. Transferring information
2. Building a relationship
3. Affecting action (getting a decision)
What are the differences in effective behavior during these interactions?
• Everyone is selling all the time. Many are not aware of it.
• Sales skills CAN be learned, (even by engineers).
• All other thing being equal, sales skills will win.
• When Sales stop, nothing happens. EVERYONE in the company must sell.
• Sales is simply good communication, where the objective is to affect action.
What types of interactions do you have in business? What percent of these have selling involved?
3.Sales and Marketing Overview
1. Marketing:
The art of making your product known to a group of potential customers, in a manner that creates an urge to buy
The art of determining the urges in your potential customers, to help you determine what product you should make (We assume you have this under control)
2. Sales:
The art of extracting an order for your product from a specific customer, and…
Making sure the customer is happy with the product so he pays for it, so that…
He may order again
4.Marketing Basics:
“The art of making your product known to a group of customers, in a manner that creates an urge to buy”
1. “Making your product known”
a. Know what your product is
b. What is your core competence that you are trying to sell
c. What do you have that your competitors don’t have
d. Tell them in a way that they can understand.
2. “to a group of potential customers”
a. Understand how and where to find these customers
b. Know the general needs (pain) of these potential customers
c. Understand why they would buy your product
d. Tell them what they want to hear
3. “in a manner that creates an urge to buy”
a. How they can buy
b. Who to call
c. When they can buy it
Rule: Good marketing appeals to the emotions of the customers
Core skills needed: Understanding of
• Culture
• Market forces
• Technology changes
• Behavior of large numbers of people
5.Sales Basics:
Sales: “The art of extracting an order from a customer, getting him to pay for the product and assuring satisfaction so that he keeps buying from you.”
Typical sales cycle:
1. Introduction
2. Bonding and Rapport. The customer must feel comfortable
3. Help the customer discover a problem that you can fix
4. Qualify his ability to buy
5. Determine how the decision to buy will be made
6. AFTER you have found out that he has a problem, that he has money to get rid of the problem, and that he can make a decision to spend the money to get rid of his problem, THEN define the requirements and your response (presentation).
7. Get the order (this is called the close) Verbal commitments are weak. Written commitments are best
8. Deliver to his expectations
9. Expand the relationship to the next problem
Ongoing Sales:
• Give the customer a superior product, at competitive cost, with timely delivery
• A customer makes his buying decisions emotionally not intellectually.
• If you don’t detect emotional interest, the sale will not happen
• Customers won’t buy from you if they dislike you. (It is not necessary that they like you, only that they Not dislike you)
Core Skill needed: Understanding of Human Nature, and ability to affect decisions.
6.Issues of Sales
1. New customers are difficult and expensive to find. Your easiest sale is always to an existing happy customer
2. Customers buy to get rid of PAIN, not for pleasure.
3. Pain = Problem x Priority x Personal
4. Salesmen are among the highest paid professionals in capitalistic economies. This is not an easy job, and requires good skills.
5. Basic sales skills: listen, find pain, empathize
6. Come to a contract that is in the customer’s best interest.
7. AFTER you have a clear understanding that your product will help assuage the customer’s pain, that he has the money to get rid of the pain, and he is or can influence the decision maker, ask for the order.
8. More contracts are lost because of failure to ask for the order than for any other reason.
9. Find and cultivate an “Inside salesman”
a. Understand his agenda
b. He will keep you informed.
c. Don’t forget to listen
10. What you say, and how you say it impacts the customer’s emotions. Emotions affect buying decisions
Rules: “Shut up, ask questions, listen, and empathize” “You establish your credibility through the questions you ask”
7.Issues of “your role” as a Salesman:
1. Always be yourself. Trying to be someone else will fail the 2 minute rule
2. Know why you win or loose an order
a. Most salesmen have grey hair and early heart attacks
b. “Random” reinforcement kills
3. Be appropriately honest
a. Don’t EVER lie. If a customer catches you lying, you will loose his trust for a LONG time.
b. Don’t volunteer negative information, unless the customer would view the holding back as lying
c. Don’t air dirty laundry
4. You will always loose some orders that you expected to win. Learn to live with it
5. Enthusiasm is contagious. Your strongest sales skill is a true belief in your product, and that it is the right decision for your customer.
6. What you say, and how you say it, affects the EMOTIONS of the customer
7. All decisions are emotional
a. Learn to Role play
b. Practice both roles, until you understand the impact of your words
c. Learn the words that work in your world.
8.Selling Situations:
The four goals of selling:
1. Gather information from the customer
2. Get the customer to admit they have a problem
3. Help the customer understand the consequences associated with the problem
4. Help the customer make a decision to act to fix the problem
A customer
• Will not change (the status quo) without pain
• Must have the money to spend to fix the pain
• Must be able to make the decision to act
For a new venture, the customer’s pain MUST BE LARGE.
No one in their right mind would buy from a new venture, unless they absolutely had to. (The value proposition must be worth the supply risk)
Rule: “No one was ever fired for buying from IBM (or Microsoft)”
9.Pain Questions:
1. Tell me ONE of your biggest concerns about __________.
2. Could you be more specific?
3. How long has this been a problem?
4. What have you done to try to fix it?
5. And that worked?
6. Over the last _____months, what has this cost your organization? (Alt: What is the impact on your organization)
7. What has the impact been on YOU personally?
8. Who else knows about the problem?
9. How do you feel about that?
10. How committed are you to fixing this problem (personally and theorganization)
11. So, what are you hoping we could do for you?
12. I’m not sure that we can do that, but… “if you contract first, we will try”.
Recap the conversation.
• You must do this in a Nurturing manner!!!
• You must be careful to leave pain if it gets too intense. You are not a shrink.
• Your job is to “take away the pain” that you uncover, with your product or service.
• These questions work like magic in many situations, including
o Sales
o Personal relationships
o Management problems
• Adjust it to your world, and learn it as a script. Don’t innovate too much in front of the customer.
10.You have to get paid.
Money:
• Most people HATE to ask about money
• Most customers will avoid talking about money
• Technical people have a real problem. Get over it
Decision:
• You have to find out who has the authority to spend the money
• Often it is not the person doing the buying
• It is imperative that you get to the decision-maker(s)
Presentation:
• After you understand the pain, money, and decision process, THEN give your presentation
Close:
• Review the conversation. Ask the customer what he wants to do.
• Keep it simple and low pressure.
11.Rule:
• If a customer lies or misrepresents about money, he is not in sufficient pain
• Real customers will discuss money openly
Some “words” that work. (Remember: the words you say affect emotions. Emotions affect decisions)
“Do you have a budget for this. Will you share it with me”?
• “No”: The customer won’t buy
• “Sure, we currently pay $….” : This is a real customer
“Who, besides you, is involved in the decision-making process”
Learn words that work in your world. Be consistent.
1. ”Effective sales uses a restricted language.”
Rules: Sales and Marketing
• You are always buying or selling
• Customers buy emotionally, not intellectually
• You establish your credibility by the questions you ask, not what you say.
• Shut up and listen.
• Listen for Pain. Empathize with the customer WHENEVER you hear pain.
• The more someone talks, the more they like you
• You cannot get emotionally involved in the sale.
• You can’t convince anyone of anything. People buy for their reasons, not yours.
• No assumptions.
• Nurture, nurture, nurture
• You must know where the money comes from, and how you will get paid
• Most engineers’ BIGGEST problem is discussing money.