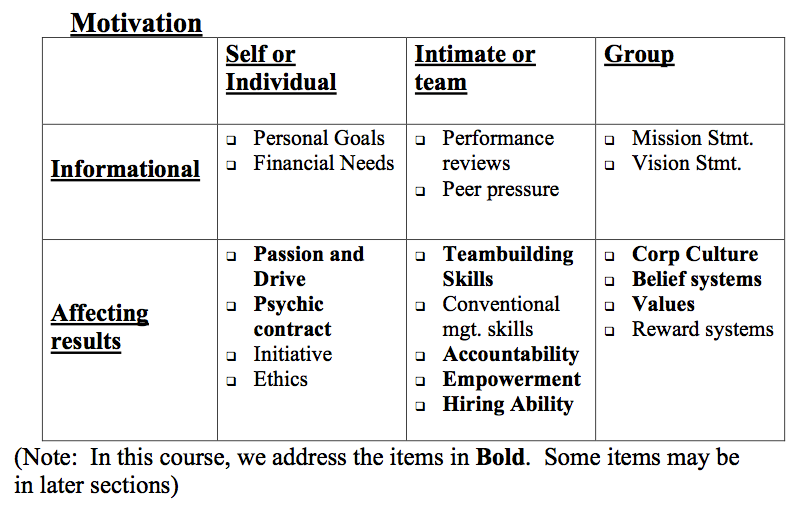
1. Big Picture of Motivation![]()
2. Myth of Assumed Maturity
3. Hierarchy of Needs
4. Psychic Contract
5. Prediction of Family Destiny
6. The Psychic Contract and the Entrepreneur
7. Response of sons of very rich men
8. How to use this information
9. Hiring: Summary and Objectives
10. Hiring experience
11. Firing
12. Rules
1.Big Picture:
Understanding Motivation is probably THE MOST IMPORTANT skill of effective people.
Understanding your own motivation has to come first.
• What drives you
• What gets you up in the morning
• How will this change as you go through life
Understanding other’s motivation is imperative to getting things done.
• What drives them
• Why will they work with (for) you
• What is in it for them
• What are the tools you have to motivate
Rule: “Everyone’s motivation is different. It changes with their particular circumstances:
The most effective people detect these core motivational issues, and adapt.
2.Myth of Assumed Maturity
This myth assumes we are all grownups. It is NOT TRUE.
• Physical Growth – Sports
• IntellectualGrowth-Educationalsystem
• Emotional Growth – Not much training in our society
Values are what drive a person. These are what he believes to be true. These come from:
• Parents
• Schools
• Church
• Professors
• Heroes
• Your boss
Hire a person who has the beliefs that you want in your organization, and holds the values that your business will hold.
• Everyone is a prisoner, locked in a cage of his own beliefs.
• You need people with the ability to see beyond their beliefs, and
• Understand reality (the competition, the market, the opportunity, etc.)
• People do not change their values easily. Your core team must have shared values.
Rule: “Hire on strong emotional skills”
3.Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Needs follow a prescribed hierarchy:
1. Food (income)
2. Safety and security
3. Love and belonging (family, status)
4. Esteem (productivity, achievement, power)
5. Self Actualization (perfection)
6. Knowledge and understanding (helping others )
7. Aesthetic Satisfaction (investigate what is really going on)
People do not perform at a higher need level, unless the lower ones are satisfied.
• Why do organizations threaten safety, and expect people to perform?
When you try to motivate, you must understand the level of the current concerns of the person you are trying to motivate.
• Fill the lower needs first. Then address the higher needs.
Rule: “Your #1 job as a leader, is to make your people feel safe”
Rule: “You must establish a sense of family (Team) before you can be productive.
4.Psychic Contract (ref: Wareham)
Nine stages in the life of an individual:
1. Programming: (Age 0-5). Head trash, Tape recorder, set values and patterns and eliminate unnecessary brain cells.
2. Contracting: (age 5-15). A psychic contract is established with the dominant people in your life (usually your parents, most often your father) about what is success.
3. Rebellion: (age 15-25). A response to the programming. May be mindless conformity (same thing)
4. Embarking: (age 25-30). Start to fulfill the contract. If tough, then fast out of the gate, since uncertain as to the path.
5. Approaching: (age 30-35). Working on it. May make life decisions based on how/hard easy the battle. E.g. forgo children, marriage, etc.
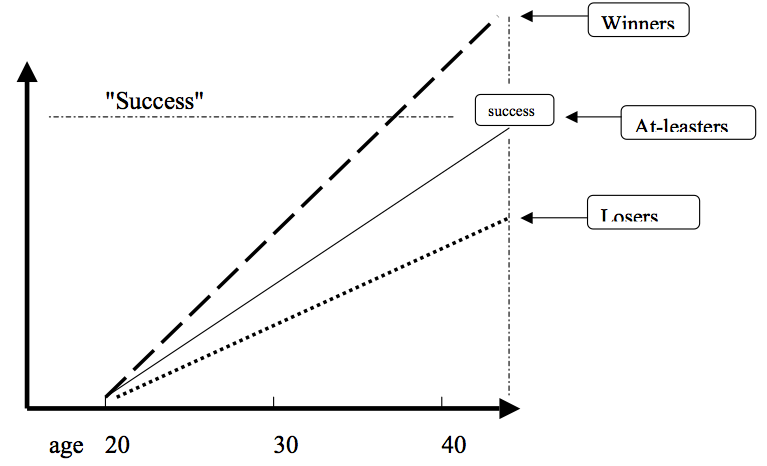
6. Winning/Losing: (age 40-45). Evaluate your success vs. your psychic contract. Often a specific goal. Winners; Losers; At-leasters:
7. Responding: (age 45-50). Suddenly see the world’s truths. Enlightenment sometimes happens
8. Apprehending: (age 50-??) Yo! What is this old age stuff?
9. Awakening/ Renewal: Able to finally enjoy life. Sudden urge to “give back”.
The “usual” contract is to “beat” your “old man”
(by at least 10% or so – more for firstborns).
5.Prediction of Family Destiny
(Psychic Contract) x (Birth Order) = Family Destiny
1. Age
2. Income
3. Tell about your parents
4. Income and occupation of parents
5. Siblings – look at place in the family, and role
a. Dominant
b. Detached
c. Rebellious
d. Dependent
6. Spouse
a. Occupation of Father-in-law
b. Spouse will have own destiny
7. Income needed to be comfortable
What is the impact of birth order on a person?
How does it show up at work?
Rules:
1. “When you hire someone, you hire his or her family destiny.”
2. “Most people operate within these bounds most of the time”
6.Psychic Contract and the Entrepreneur
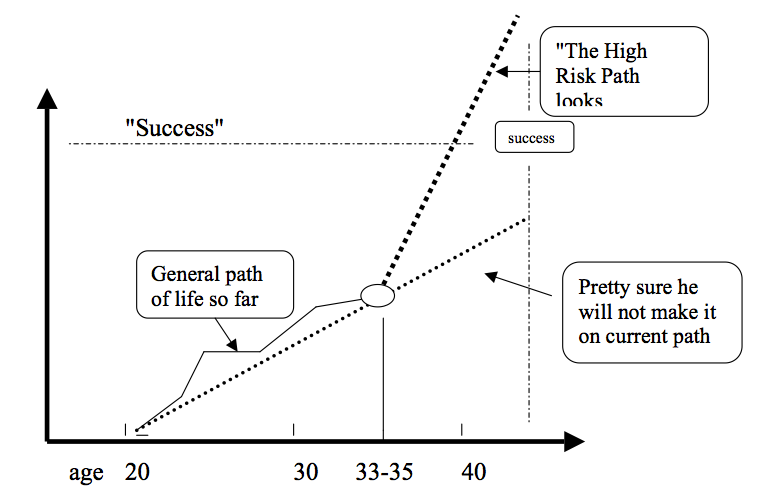
The average age for someone to “start a business” is 33-35.
• Surprisingly, the internet age has not changed this significantly
• Why then?
Winners:
• “I made it, what is life really about”
• “Let’s sail to Tahiti”
Losers: “I would have done better if not for (spouse, Vietnam, you pick)
At-leasters:
• “I may not be as successful as my Dad, but I am a better father”
• “He was wealthier, but I am more famous”
• “I decided to pursue an academic career”
Psychic Contract and the Entrepreneur
If the entrepreneur sees that the opportunity will give him a reasonable chance to make his contract, he will do the behaviors to get there.
Key questions:
• What is his/her contract?
• Where is he/she now?
(This is the most important page in this book)
7.Typical response of sons* of very rich men
1. Try to make the contract
2. Rebel. Live to different values
3. Torpedo the family business
4. Mano-e-mano. Outperform in same game
5. Success in a non-competing field. (Healthy)
6. Chose the “family” contract as “at-leaster”
*It appears that daughters often have 2 contracts, one with the “father” on success, and one with the “mother” on family. A lot of the struggle that women seem to have in the workplace is the conflict between these two contracts. Men do not usually have as strong a “family contract”, except as an “at-leaster”.
I have not seen anything written on this, but this was the report from an ad hoc “female working group at MIT”, fall 1997. Unfortunately, most work in this area has been done on men.)
This “Psychic Contract” resonates with about 75% of people. If it doesn’t resonate with you, which it may not, use the knowledge of it to try to understand what drives and motivates others.
Note: The “Father” and “Mother” can be authority figures other than the actual parents. Grandparents, older siblings, mentors, etc. can often provide the hurdle for success.
Second Order Contracts,
1. Missing Father
a. You can make it into “anything” you want
2. No Approval by Father
a. A cause of “serial entrepreneurship”
3. Immigrant Father
a. Takes the Father’s success off the table
4. Pushed Contract
a. “You will be a doctor, not a schmuck like your father”
Making the Contract
Once you make the contract, the drive goes away.
– The reduction in Drive intensity is astonishing
You would rather-
– Mentor and advise
– Write a book – Retire
– Help others be successful
– Do research
– Give back
– Focus on Family
8.How to use this information
Use knowledge of Psychic Contract for:
– Hiring
– Motivation
– Predicting disaster
– Negotiating
– Mentoring
– Recognizing whose team to join
Rule: “Your most expensive employee is mediocre”
Rule: “You want to join a team where the leader will do the behaviors to reach the goal
The “Peter Principle”
• (old) “people rise to their level of incompetence”
• (new) “People rise until they make their contract. After that they will no longer do the behaviors to succeed at the next higher level”
How to find people for your team:
• Networking
• Job Fairs
• Classified Ads
• Headhunters After their first job, most people are found from networking (roughly 70%)
Objectives in Hiring People
What you want in an employee or team member:
1. Common Sense
2. Competence
3. Productive
4. Works as a team
Wrong assumptions about people:
1. Instant insight
2. Assumed consciousness about what is going on
3. Psychic equilibrium (most people are poorly adjusted)
4. Assume that problems are there, will always be there, and work around them.
How do you eat an apple with spots?
Rule: “Hire on Ability to Learn, Passion and Drive, and Motivation”
Rule: “People don’t change. Accept it, and work with it”
9.Summary of Hiring:
You are “hiring” whenever you are putting together a team to implement a project. This can be “hiring” from outside your organization, or “hiring” from inside our organization.
This is your most important job.
• Your success depends on other people
• Learn how to do it well, or fail
• You cannot succeed without control over your team
Job #1: Team, Team, Team
Job #1a: Hiring, Hiring, Hiring
Hiring:
• Go for thinking, aptitude, drive; NOT knowledge
• You must develop a people detector
• The cost of incompetence can be the success of your project
Benchmark:
• Test for relevant knowledge
• This is not necessarily YOUR knowledge
• Use Professional exams
• Protect yourself from bias
Your Job:
• Hire
• Teach
• Lead
• Inspire
• Get out of the way
What process for “hiring” do you use today?
Rule: The biggest risk is to hire people “just like me”
10.Hiring experience
The importance of testing: (Based on my experience in hiring technical people)
Test: 20 questions from Graduate Record Exam in Engineering, not too tough, questions related to the job requirements:
• Average score of “competent engineers in our organization” = 16 (range 11-20). Good correlation with actual performance. (The “A” performers scored highest, the “C” performers scored lowest.)
• Actual statistics for hiring process: (All graduate engineers in the Boston area)
• You get a score of “4” just by guessing, with average luck!!
Rule: “Do not assume that a college degree means anything!”
11.Firing:
Unfortunately, this is as important as hiring.
Every organization needs an appropriate amount of “turnover”
• Inflow of new ideas and perspectives
• Elimination of non-performers
• Reduction of mediocrity
• Outflow of Intellectual property- makes you move faster
• Expands your influence through expatriates
The “average” technical person changes jobs every 1.5 yrs. in Silicon Valley, every 4.5 yrs. on the East Coast. Which is more competitive today?
• There are some good benchmarks: (e.g. GE, Marine Air Core, etc)
• 10% to 25% per year should be actively removed by management decision
• This should be done in a way that strengthens both the organization and the individual
• The remaining organization becomes more loyal (not less) and healthier
• You retain your right to fire for performance.
Rule for good firing: “Send out ambassadors, not refugees”
When an executive leaves GE, he/she often becomes a very loyal customer for GE products at his new company.
• What are the penalties for not actively managing your workforce?
• What happens when attrition is “offered”, or conducted only by seniority?
12.Rules: People, Motivation, and Hiring
• Hire on strong emotional skills, teach the technical skills
• Hire on ability to learn, and ability to do.
• Your most expensive employee is a mediocre employee.
• Your #1 job as a leader is to make your people feel safe
• When you hire someone, you hire their family, and their family destiny
• People do not change. Accept it, and work with it.
• Check motivation. A capable, smart, unmotivated employee is worthless.
• Test!!! Take nothing for granted. Resumes are a poor indicator of future performance.
• Fire well. Send out ambassadors, not refugees